Introduction
Picture this: You’re standing in front of your bathroom mirror, noticing changes in your body that don’t quite make sense. Irregular periods, unexpected weight gain, acne that reminds you of your teenage years – could these seemingly unrelated symptoms be connected? For millions of women worldwide, these experiences often point to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), a condition that affects up to 10% of women of reproductive age.
What Exactly is PCOS?
PCOS isn’t just another medical acronym – it’s a complex hormonal condition that can affect various aspects of your health and well-being. Think of your endocrine system as an intricate orchestra, where hormones are the musicians. In PCOS, some of these musicians are playing slightly off-key, creating a hormonal imbalance that can affect your entire body.
According to the Mayo Clinic, PCOS occurs when your ovaries produce an unusual amount of androgens, male hormones that are typically present in women in small amounts.
The Tell-Tale Signs: PCOS Symptoms
“I knew something was wrong, but I couldn’t put my finger on it,” – this is a sentiment I often hear from women discussing their PCOS journey. Let’s break down the most common symptoms:
Primary Symptoms
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles
- Periods that come and go as they please
- Cycles longer than 35 days
- Fewer than 8 periods per year
- Excess Androgen Signs
- Unwanted hair growth (hirsutism)
- Acne
- Male-pattern baldness
- Polycystic Ovaries
- Multiple fluid-filled sacs (follicles) on ovaries
- Enlarged ovaries
Beyond the Basics: Lesser-Known PCOS Symptoms
What many don’t realize is that PCOS can affect more than just your reproductive system. According to Johns Hopkins Medicine, women with PCOS might also experience:
- Skin tags
- Dark patches on skin (acanthosis nigricans)
- Mood changes
- Sleep problems
- Headaches
- Pelvic pain
The Mystery Behind PCOS: Understanding the Causes
Remember that puzzle I mentioned earlier? Well, the cause of PCOS is perhaps its most puzzling piece. While researchers haven’t pinpointed an exact cause, several factors appear to play crucial roles:
Genetic Factors
If your mother or sister has PCOS, you’re more likely to develop it too. Research from the National Institutes of Health suggests that several genes might contribute to the condition.
Insulin Resistance
Think of insulin as a key that unlocks your cells to let in glucose. In many women with PCOS, this key doesn’t work quite right, leading to:
- Higher insulin levels
- Increased androgen production
- Difficulty maintaining a healthy weight
Inflammation
Chronic low-grade inflammation in women with PCOS can stimulate polycystic ovaries to produce androgens.
The Four Types of PCOS: Yes, There’s More Than One!
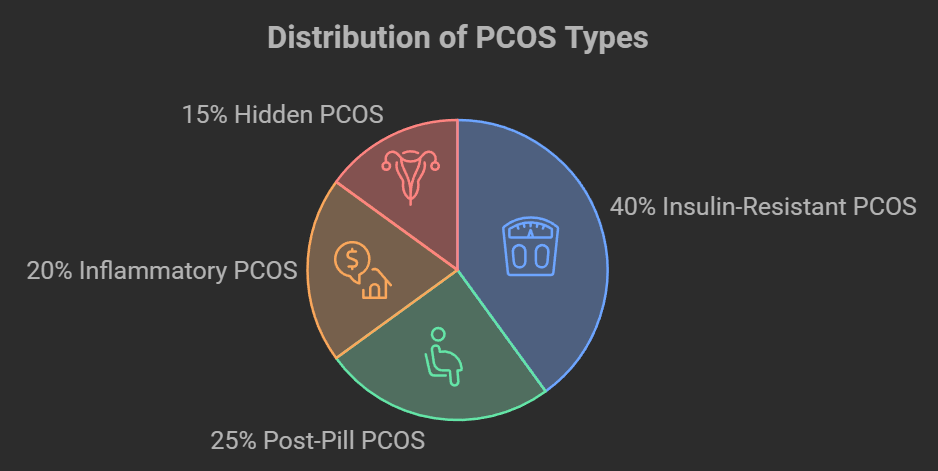
Something that often surprises my readers is learning that PCOS isn’t a one-size-fits-all condition. According to recent research, there are four main types:
- Insulin-Resistant PCOS
- Most common type
- Associated with weight gain
- Responds well to lifestyle changes
- Post-Pill PCOS
- Occurs after stopping hormonal birth control
- Often temporary
- May resolve on its own
- Inflammatory PCOS
- Linked to chronic inflammation
- Often associated with diet and lifestyle factors
- May improve with anti-inflammatory approaches
- Hidden PCOS
- Symptoms present without cysts on ovaries
- Can be harder to diagnose
- Requires comprehensive testing
Common Questions About PCOS Symptoms and Signs
PCOS Discharge and Physical Signs
Many women ask, “What does PCOS discharge look like?” While PCOS can affect vaginal discharge, variations are normal and not necessarily indicative of the condition. If you notice unusual changes, consult your healthcare provider.
Understanding PCOS Weight Distribution
“What does a PCOS belly look like?” is another common question. Women with PCOS often experience weight gain around the midsection due to insulin resistance. This “apple-shaped” body type can be managed through targeted exercise and diet modifications.
PCOS Pain and Discomfort
“What does PCOS pain feel like?” PCOS-related pain can manifest as:
- Pelvic discomfort
- Menstrual cramping
- Lower back pain
- Ovulation pain

PCOS and Your Daily Life
Emotional Well-being
Does PCOS make you cry a lot? The hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS can affect mood and emotional stability. Many women experience:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Mood swings
- Emotional sensitivity
Diet and Nutrition Guidelines
Foods to Embrace and Avoid
Can I drink milk in PCOS? Can I eat rice in PCOS? Can I eat eggs in PCOS? Here’s a comprehensive guide:
PCOS-Friendly Foods:
- Eggs (rich in protein and nutrients)
- Brown rice (in moderation)
- Plant-based milk alternatives
Foods to Limit:
- Full-fat dairy products
- Refined carbohydrates
- Sugary beverages
Exercise Recommendations
Which exercise is best for PCOS? Focus on:
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
- Strength training
- Yoga (especially poses beneficial for PCOS)
- Regular cardio activities
Natural Approaches to PCOS Management
Herbal Remedies
PCOS tea options include:
- Spearmint tea (may help reduce androgen levels)
- Green tea (supports metabolism)
- Cinnamon tea (helps with insulin sensitivity)
Supplements and Natural Treatments
- Ovasitol for PCOS
- Inositol supplements
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Vitamin D
Medical Testing and Diagnosis
Blood Investigations for PCOS
Common blood tests include:
- Hormone level testing
- Insulin resistance markers
- Thyroid function tests
- Cholesterol levels
Hydration and PCOS
Proper hydration plays a crucial role in:
- Hormone balance
- Insulin sensitivity
- Weight management
- Overall health
Special Considerations
PCOS Throughout Life Stages
- At what age PCOS ends? While PCOS is a lifelong condition, symptoms may change after menopause
- Can PCOS go away on its own? While it doesn’t typically resolve spontaneously, symptoms can be effectively managed
- Is PCOS a lifelong disease? Yes, but with proper management, you can live a normal, healthy life
Additional Treatment Options
- Hysterectomy for PCOS: Usually only considered in severe cases with other underlying conditions
- PCO Syndrome vs. PCOS: Understanding the difference between polycystic ovaries and the syndrome
- Adrenal gland PCOS: The role of adrenal hormones in PCOS
Resources and Support
- PCOS cookbook recommendations
- PCOS diet plan PDF resources
- Support groups and communities
- Tracking apps and tools
Diagnosis: Putting the Pieces Together
Getting diagnosed with PCOS can feel like a relief and a challenge all at once. The Cleveland Clinic outlines the diagnostic criteria, known as the Rotterdam criteria:
The Rotterdam Criteria
You must have at least two of these three conditions:
- Irregular or absent periods
- Signs of excess androgens
- Polycystic ovaries on ultrasound
Common Diagnostic Tests
- Physical exam
- Pelvic exam
- Blood tests for hormones
- Ultrasound
- Glucose tolerance test
Treatment Options: Your Roadmap to Managing PCOS
Here’s the good news: while PCOS isn’t curable, it’s definitely manageable. Treatment plans are typically personalized and may include:
Lifestyle Modifications
- Regular exercise (30 minutes, 5 days a week)
- Balanced diet rich in:
- Lean proteins
- Whole grains
- Vegetables
- Healthy fats
- Stress management
- Adequate sleep
Medications
According to the American Academy of Family Physicians, common medications include:
- Birth control pills
- Metformin
- Anti-androgen medications
- Fertility medications (if trying to conceive)
Living with PCOS: Real Talk
Let’s have an honest conversation about what it’s really like living with PCOS. Some days are harder than others, and that’s okay. Here are some practical tips I’ve gathered from women managing PCOS successfully:
Daily Management Strategies
- Track Your Symptoms
- Use a period tracking app
- Keep a symptom diary
- Monitor your energy levels
- Build Your Support System
- Join PCOS support groups
- Connect with others online
- Keep your healthcare team informed
- Focus on Mental Health
- Practice self-compassion
- Consider counseling if needed
- Engage in stress-reducing activities
PCOS and Fertility: There’s Hope
One of the most common concerns I hear is about fertility. While PCOS can make conception more challenging, many women with PCOS successfully become mothers. According to research, various treatment options can help, including:
- Ovulation induction medications
- Lifestyle modifications
- Assisted reproductive technologies
The Future with PCOS: Looking Ahead
Research into PCOS continues to evolve, bringing new hope and treatment options. The Women’s Health Office regularly updates its guidelines as new discoveries emerge.
Conclusion: Your PCOS Journey
Remember, having PCOS doesn’t define you – it’s just one part of your health journey. With the right information, support, and treatment plan, you can live a full, healthy life with PCOS. Don’t hesitate to reach out to healthcare providers and support groups as you navigate this journey.